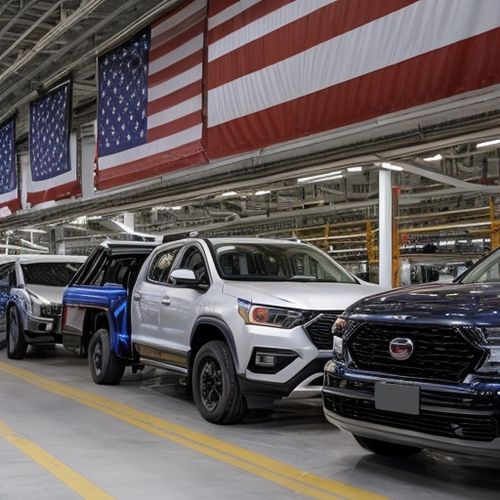
As President Donald Trump’s 25% tariffs on imported vehicles remain in effect, the automotive industry is bracing for significant global implications. Despite a pullback on other country-based levies, the tariffs on vehicles and automotive parts are expected to have far-reaching effects on sales, prices, and production costs.
Expected Drop in Vehicle Sales and Increased Costs
Analysts predict a substantial drop in vehicle sales, with estimates ranging in the millions. According to research from Wall Street and automotive analysts, the industry is expected to face increased costs of over $100 billion. Felix Stellmaszek, Boston Consulting Group’s global lead of automotive and mobility, highlighted the long-lasting structural shift driven by these policies, potentially making 2025 one of the most consequential years for the auto industry.
Tariff Details and Cost Implications
The tariffs, which went into effect on April 3, include a 25% levy on imported vehicles and will be followed by similar tariffs on automotive parts starting May 3. The Center for Automotive Research estimates that these tariffs will increase costs for US automakers by $107.7 billion, with $41.9 billion of that burden falling on Detroit automakers General Motors, Ford, and Stellantis.
Impact on Consumers and Market Dynamics
The increased costs are expected to be passed on to consumers, leading to higher prices for both new and used vehicles. Goldman Sachs analysts predict that new vehicle prices in the US will rise by $2,000 to $4,000 over the next six to twelve months. This price increase could further soften consumer demand, especially given the already high cost of new vehicles, which average nearly $50,000 according to Cox Automotive.
Automakers’ Responses
Automakers have responded to the tariffs in various ways. Domestic manufacturers like Ford and Stellantis have announced temporary deals for employee pricing to mitigate the impact. In contrast, Jaguar Land Rover has ceased US shipments, while Hyundai has pledged not to raise prices for at least two months. These strategies aim to ease consumer concerns and maintain market stability.
Broader Economic Impact
The tariffs are expected to have broader economic implications beyond the automotive industry. Telemetry, an auto advisory firm, anticipates that the higher production costs will result in over 2 million fewer vehicles sold annually in the US and Canada. This reduction in sales will have ripple effects on the broader economy, driven by higher prices across various sectors, which will limit consumer spending power.
The automotive industry is navigating a complex landscape as it adjusts to the new tariff policies. While some manufacturers are finding ways to absorb or mitigate the increased costs, the long-term impact on vehicle sales, consumer prices, and production remains uncertain. As the industry adapts, the broader economic implications will continue to unfold, highlighting the need for clarity and stability in trade policies.

By Samuel Cooper/Apr 14, 2025

By Michael Brown/Apr 14, 2025
By Emma Thompson/Apr 14, 2025

By David Anderson/Apr 14, 2025

By Megan Clark/Apr 14, 2025

By Emma Thompson/Apr 14, 2025

By Thomas Roberts/Apr 14, 2025

By Rebecca Stewart/Apr 14, 2025

By Natalie Campbell/Apr 14, 2025

By Laura Wilson/Apr 14, 2025

By Ryan Martin/Apr 14, 2025

By Elizabeth Taylor/Apr 14, 2025

By Laura Wilson/Apr 14, 2025

By Sophia Lewis/Apr 14, 2025

By Laura Wilson/Apr 14, 2025

By Elizabeth Taylor/Apr 14, 2025

By Amanda Phillips/Apr 14, 2025

By Sarah Davis/Apr 14, 2025

By Samuel Cooper/Apr 14, 2025